Continuous Theta
Burst Stimulation (cTBS) is a specific protocol of repetitive transcranial
magnetic stimulation (rTMS) that is used to modulate cortical excitability and
induce neuroplastic changes in the brain. Here is a detailed explanation of
Continuous Theta Burst Stimulation:
1. Definition:
o cTBS: Continuous
Theta Burst Stimulation is a patterned form of rTMS that involves delivering
bursts of magnetic pulses at a specific frequency and intensity over a
continuous period of time to a targeted area of the brain. It is characterized
by the application of theta-burst patterns of stimulation.
2. Stimulation
Parameters:
o Theta Burst
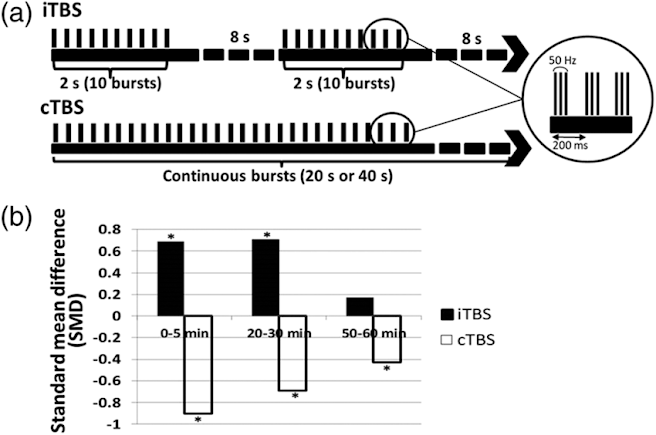
Pattern: The
theta burst pattern consists of bursts of three pulses at 50 Hz repeated at a
theta frequency (5 Hz). This pattern is delivered continuously over a specified
duration, typically ranging from several seconds to minutes, depending on the
research or clinical protocol.
o Intensity and
Duration: The
intensity of cTBS is usually set as a percentage of the individual's resting
motor threshold, ensuring that the stimulation is tailored to the specific
cortical excitability of the target area. The duration of cTBS can vary based
on the desired effects and experimental design.
3. Mechanism of
Action:
o Inhibitory Effect: cTBS is
primarily known for its inhibitory effects on cortical excitability. By
delivering continuous theta burst patterns, the stimulation leads to a
reduction in neuronal firing rates and synaptic transmission in the targeted
brain region.
o Long-Lasting
Effects: cTBS
has been shown to induce long-lasting changes in cortical excitability, with
inhibitory effects persisting beyond the stimulation period. This ability to
modulate neural activity and induce plastic changes makes cTBS a valuable tool
for studying brain function and potential therapeutic applications.
4. Applications:
o Research: cTBS is widely
used in research settings to investigate the role of inhibitory mechanisms in
cortical function, neural plasticity, and motor learning. Researchers utilize
cTBS to study the effects of cortical inhibition on cognitive processes, motor
control, and sensory functions.
o Therapeutic
Potential: In
clinical applications, cTBS is being explored as a potential treatment strategy
for neurological and psychiatric disorders. By modulating cortical excitability
and neural networks, cTBS may offer therapeutic benefits for conditions such as
depression, chronic pain, stroke recovery, and movement disorders.
5. Clinical Studies:
o Depression: cTBS has shown
promise as a non-invasive treatment for depression, particularly in individuals
who are resistant to traditional therapies. By targeting specific brain regions
implicated in mood regulation, cTBS may help alleviate depressive symptoms and
improve overall well-being.
o Neurorehabilitation: In the field of
neurorehabilitation, cTBS is being investigated as a potential adjunct therapy
to enhance motor recovery following stroke, traumatic brain injury, or other
neurological conditions. By modulating cortical plasticity, cTBS may facilitate
motor relearning and functional recovery.
In summary,
Continuous Theta Burst Stimulation is a specialized form of rTMS that exerts
inhibitory effects on cortical excitability and induces long-lasting changes in
neural activity. With applications in research and clinical settings, cTBS
offers insights into brain function, neuroplasticity, and potential therapeutic
interventions for a range of neurological and psychiatric disorders.

Comments
Post a Comment